Unlock the Evolution of Geographical Thought: Ancient to Modern Insights

1. Introduction to Evolution of Geographical Thought
Geography is not just about maps and landscapes. It’s a way to understand our world and how we interact with it. The study of geography has evolved over thousands of years, reflecting changes in technology, society, and thought. This Evolution of Geographical Thought E-Book delves into the history of geographical thought, highlighting the major milestones and ideas that have shaped our understanding of the Earth.
2. Early Beginnings: Ancient Civilizations
Geographical thought has its roots in the ancient civilizations of Mesopotamia and Egypt. These early societies made significant strides in understanding their world.
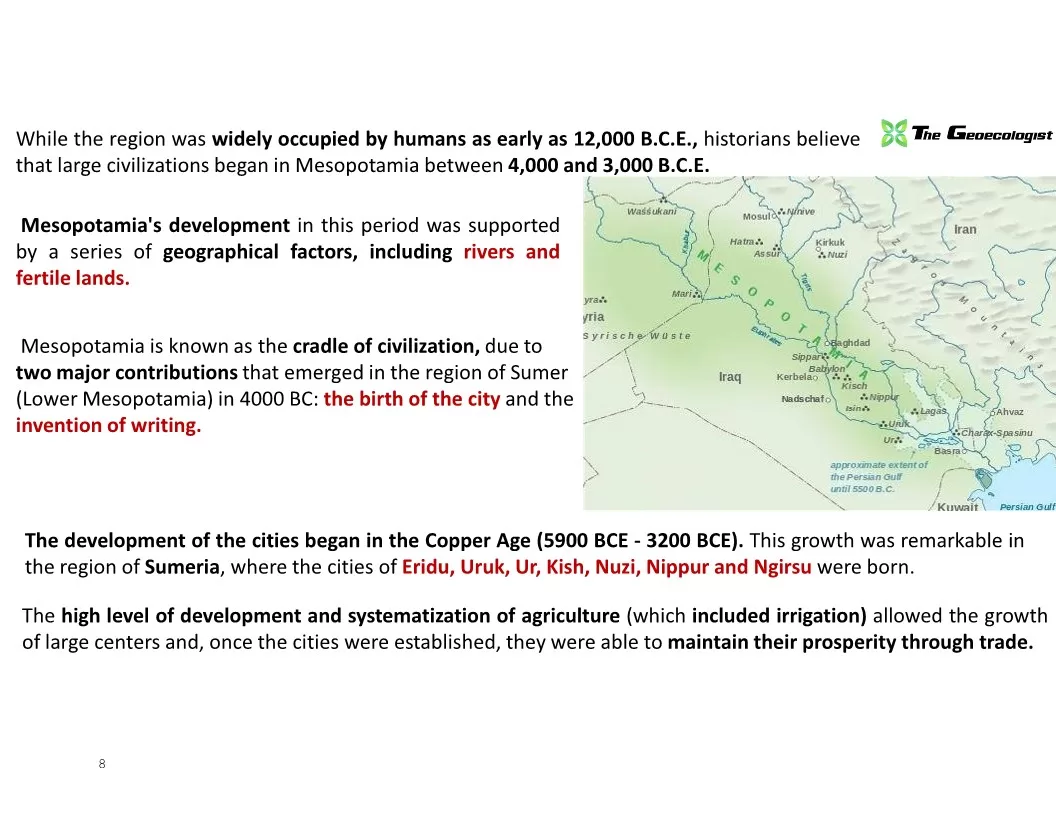
- Mesopotamia: Known as the “cradle of civilization,” Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq) saw early forms of geographical thought. The Sumerians and Babylonians developed early maps and recorded observations about their environment.
- Egypt: Ancient Egyptians used geographical knowledge for practical purposes such as irrigation and navigation. They mapped out the Nile River and surrounding areas, crucial for their agricultural and trading activities.
Key Points:
- Early maps were often simple and functional.
- Geographic knowledge was mainly for practical uses like farming and trade.
3. Greek and Roman Contributions
Greek and Roman scholars made foundational contributions to geographical thought. Their work laid the groundwork for modern geography.
- Greek Scholars:
- Thales: One of the first Greek philosophers, Thales, proposed that the Earth floated on water. He is often credited with early ideas about the natural world.
- Anaximander: Anaximander created one of the earliest known maps of the world. He also introduced the concept of the “apeiron” or the boundless, which influenced later geographical thought.
- Eratosthenes: A significant figure, Eratosthenes calculated the Earth’s circumference with remarkable accuracy. He also coined the term “geography.”
- Roman Scholars:
- Strabo: Strabo wrote “Geographica,” a comprehensive work covering various regions of the known world. His descriptions of places and people were influential.
- Ptolemy: Claudius Ptolemy’s “Geographia” compiled knowledge from earlier scholars and introduced concepts like latitude and longitude. His maps and writings influenced geographical understanding for centuries.
Key Points:
- Greek scholars contributed early theories and maps.
- Roman scholars expanded and refined geographical knowledge.
4. The Dark Ages and Arab Renaissance
The Dark Ages in Europe were a period of relative stagnation in geographical thought. However, the Arab world experienced a renaissance in learning and made significant contributions.
- The Dark Ages:
- During this period, geographical knowledge in Europe was limited. Much of the knowledge from earlier periods was lost or forgotten.
- Arab Renaissance:
- Al-Idrisi: A prominent Arab geographer, Al-Idrisi created the “Tabula Rogeriana,” one of the most detailed maps of the medieval world. His work combined knowledge from various cultures.
- Ibn Battuta: An explorer and scholar, Ibn Battuta traveled extensively across Africa, Asia, and Europe. His detailed accounts provided valuable insights into the regions he visited.
Key Points:
- European geographical thought stagnated during the Dark Ages.
- The Arab world preserved and expanded geographical knowledge.
5. The Age of Exploration
The Age of Exploration marked a significant shift in geographical thought. European explorers ventured into unknown territories, leading to new discoveries and mapping.
- Christopher Columbus: Columbus’s voyages to the Americas in 1492 expanded the known world dramatically. His explorations led to the mapping of previously unknown continents.
- Vasco da Gama: Da Gama’s journey to India opened new trade routes and increased European knowledge of the Indian Ocean and surrounding regions.
- Ferdinand Magellan: Magellan’s expedition completed the first circumnavigation of the Earth, providing new insights into global geography.
Key Points:
- Explorations led to the discovery of new lands and sea routes.
- Mapping and geographical knowledge expanded significantly.
6. Pre-Modern to Modern Transitions
As we moved from the pre-modern to the modern era, geographical thought became more systematic and scientific.
- Varenius and Kant: These philosophers laid the groundwork for modern geographical thought. Varenius emphasized the importance of systematic study, while Kant introduced ideas about space and place.
- Humboldt and Ritter: Alexander von Humboldt and Karl Ritter are considered pioneers of modern geography. Humboldt’s work focused on the relationship between nature and human activity, while Ritter emphasized regional geography.
Key Points:
- Philosophers and scientists began to systematize geographical knowledge.
- Modern geography became more focused on scientific and empirical methods.
7. Diverse Schools of Thought
Geographical thought has diversified into various schools, each offering different perspectives and methodologies.
- German School: Led by figures like Friedrich Ratzel and Carl Ritter, this school emphasized empirical research and the relationship between geography and society.
- French School: Paul Vidal de la Blache’s work focused on regional analysis and cultural landscapes. His approach highlighted the importance of human-environment interactions.
- British School: Influenced by thinkers like Halford Mackinder and Ellen Churchill Semple, this school emphasized geopolitics and environmental determinism.
- American School: Characterized by pragmatic approaches, figures like William Morris Davis and Carl Sauer contributed to applied geography and regional studies.
Key Points:
- Different schools of thought offer varied perspectives on geography.
- Each school contributed unique methodologies and insights.
8. Global Perspectives: Indian Contributions
Indian scholars have also made significant contributions to geographical thought, enriching our understanding of the world.
- Chanakya: An ancient Indian scholar, Chanakya, wrote about geography and economics in his work, the “Arthashastra.” His ideas influenced governance and strategic planning.
- Radhakamal Mukerjee: A modern Indian geographer, Mukerjee’s work focused on the relationship between environment and human activity in South Asia.
Key Points:
- Indian scholars contributed to both ancient and modern geographical thought.
- Their work expanded understanding of regional and global geography.
9. Contemporary Debates and Paradigms
Geographical thought continues to evolve with contemporary debates and new paradigms.
- Quantitative Revolution: This period saw the introduction of mathematical models and statistical techniques in geography. It marked a shift towards more rigorous and empirical methods.
- Environmentalism and Feminism: Recent debates include environmentalism, which examines human-environment interactions, and feminism, which explores gendered dimensions of space and place.
Key Points:
- Geography now incorporates diverse methodologies and perspectives.
- Contemporary debates address complex issues in human-environment interactions.
10. Key Takeaways of Evolution of Geographical Thought
- Geographical thought has evolved from simple maps to complex scientific analyses.
- Key figures like Eratosthenes, Ptolemy, and Humboldt have significantly influenced the field.
- Different schools of thought offer varied perspectives on geography.
- Contemporary geography continues to address modern challenges and debates.
11. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on
Evolution of Geographical Thought
1. What is the importance of geographical thought? Geographical thought helps us understand the Earth and our place within it. It influences everything from mapping and navigation to environmental management and policy-making.
2. How did ancient civilizations contribute to geography? Ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia and Egypt made early contributions by developing maps and understanding their environment for practical purposes.
3. What was the impact of the Age of Exploration on geography? The Age of Exploration expanded the known world significantly. Explorers like Columbus and Magellan provided new insights into previously uncharted regions.
4. How did the Arab Renaissance influence geography? The Arab Renaissance preserved and expanded geographical knowledge during the Dark Ages. Scholars like Al-Idrisi and Ibn Battuta made significant contributions to mapping and exploration.
5. What are the major schools of thought in geography? The major schools include the German, French, British, and American schools, each offering different methodologies and perspectives on geographical research.
Key Features Of Evolution of Geographical Thought
- In-Depth Analysis: The e-book offers a thorough analysis of geographical thought throughout history.
- Illustrative Maps and Figures: It includes maps and figures that illustrate the development of geographical ideas and discoveries.
- Expert Insights: Written by Dr. Krishnanand, the e-book draws on extensive expertise and research, providing authoritative insights into the field of geography.
Key Takeaways From Evolution of Geographical Thought E-Book
- Historical Perspective: Readers will gain a deep understanding of how geographical thought has evolved over time.
- Influential Figures: The e-book highlights key figures and their contributions, showing how their ideas shaped modern geography.
- Global Contributions: It emphasizes the global nature of geographical development, including contributions from various cultures and regions.
Conclusion On Evolution of Geographical Thought E-Book
“Evolution of Geographical Thought (Revised)” by Dr. Krishnanand is a valuable resource for anyone interested in the history and development of geography. It offers a detailed and accessible exploration of how geographical ideas have transformed from ancient times to the present day. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or simply curious about the subject, this e-book provides a comprehensive and engaging look at the evolution of geographical thought.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Evolution of Geographical Thought E-book
1. What is the focus of “Evolution of Geographical Thought (Revised)” by Dr. Krishnanand? The e-book focuses on the historical development of geographical thought, exploring how ideas and theories about geography have evolved over time.
2. Who would benefit from reading this Evolution of Geographical Thought e-book? Students, researchers, and anyone interested in the history of geography will find this e-book valuable. It provides insights into key figures, events, and concepts in geographical thought.
3. What topics are covered in the Evolution of Geographical Thought e-book? The e-book covers topics such as ancient geographical knowledge, Greek and Roman contributions, the Arab Renaissance, the Age of Exploration, diverse schools of thought, and contemporary debates in geography.
4. How does the e-book present historical information? The Evolution of Geographical Thought e-book presents historical information through detailed analysis, maps, figures, and expert insights, making it accessible and engaging for readers.
Follow The Author On Facebook
Subscribe The Author On Youtube
Follow The Author On Instagram

















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.